How to setup and configure ESLint
In this post, we will teach you how to setup and configure ESLint.
How to setup and configure ESLint – Prerequisites
What is ESLint?
ESLint is a static code analysis tool that identifies and reports code patterns based on a pre-defined ruleset. It does this for ECMAScript and JavaScript files. Its general purpose is to keep your code more consistent due to the rule enforcements and to ensure your code is syntactically correct .
Let’s take a look at an example of EsLint in action.
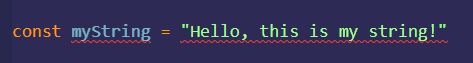
As you might have noticed, we have two squiggly lines. These lines indicate an issue within our codebase. Upon further inspection, we can see the error messages.

From these messages, we can deduce that ESLint wants us to use single quotes, instead of double-quotes. Next to that, we also forgot a semi-colon to end our code-line with.
Because ESLint runs in your whole project, this means that your everything within your project will get the errors shown above, enforcing you to use the same rules and code styles everywhere in your project.
Let’s get started with setting up ESLint into our project!
Installing ESLint
Before we have everything up and running, we need a project where we can install ESLint.
Create a new directory and initialize an empty Node project inside of it.
$ mkdir my-eslint-app $ cd my-eslint-app $ npm init -y
Note: we use the -y flag to skip the setup questions and instead give us the bare minimal project structure.
Now that we have an empty Node project, we can install ESLint!
Inside your my-eslint-app directory, run the following command
$ npm install eslint --save-dev
Note: we use --save-dev to install it under our devDependencies. In a production build, this package won’t be installed. This is exactly what we want.
After ESLint finished installing, you’re not quite there yet. ESLint won’t run out of the box without a configuration file.
To get the configuration file inside our project, we run the following command.
$ npm install -g npx $ npx eslint --init
The first line might come as a surprise. We’re installing NPX. We will be using this to execute NPM package binaries. When we installed ESLint, we were also given an executable located in node_modules/eslint/bin/eslint.js. In order to run this file and to create our config file, we use NPX.
Running the second command, npx eslint --init will give us some option prompt inside the terminal. We will pick the following options.
To check syntax, find problems, and enforce code style JavaScript modules (import/export) None of these No Node Use a popular style guide Airbnb JavaScript Yes
Your terminal should look a bit like the following

Testing our ESLint install
After everything finished installing, you should now see a .eslintrc.js file. If you don’t see this file, make sure you can see hidden files. Usually, you can enabled this with the keyboard shortcut CTRL + H for Windows and Linux and Command + Shift + . for macOS.
Take a quick glance inside your .eslintrc.js file. Notice how it’s a bit empty? All our rules are inside the AirBNB config we downloaded during our setup. Inside the rules object, we can define our own custom rules but let’s leave this be for now.
Let’s start creating a simple script to see ESLint in action.
Inside your my-eslint-app root, add the following file index.js with the following line.
console.log("OBZ is cool!");
You should see a red squiggly line underneath our string. AirBNB enforces the use of singlequotes for strings which is why we get this error. If we change "OBZ is cool!" to 'OBZ is cool!' we see that the red line goes away!
If you’re using Visual Studio Code and you’re getting a line-ending error, check the CLRF/LF option in the bottom right of the application.

Adding a custom rule
Let’s do one final thing, open up your .eslintrc.js file and add the following under the rules section so that your file looks like this.
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
},
extends: [
'airbnb-base',
],
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 12,
sourceType: 'module',
},
rules: {
indent: [
'error',
2,
],
'linebreak-style': [ /* Optional for Windows users */
'error',
'windows',
],
},
};
What we’ve done here is set the indents of our files to use two spaces instead of the usual four. See how easily you can configure your code conventions?
We have succesfully installed and configured ESLint into our project. This same logic can apply to already existing projects and will thus work everywhere you want it. Just make sure to not change your convention half way through your project!








