Why you should use Rustscan for port scanning
In this article, we will discuss a tool called RustScan.RustScan is an open-source software tool that scans networks for open TCP/UDP ports. The advantage of RustScan over other port scanners is that RustScan is way faster in scanning ports and hosts than its competitors.
How to install RustScan
You can install RustScan using different methods. You can install RustScan using Docker or the Debian package manager to install RustScan on operating systems like Ubuntu and Kali Linux. Below are the installation instructions for Docker and the Debian Package Manager.
How to install using Docker
The best way to install RustScan is by using Docker. You can install Docker using the following guide. After installing Docker, run the following commands to pull the image for the 2.0.0. version.
docker pull rustscan/rustscan:2.0.0After pulling the image, you can run RustScan by running:
docker run -it --rm --name rustscan rustscan/rustscan:2.0.0 <rustscan arguments here> <ip address to scan>Since we do not want to run such a long command each time, we will be creating an alias
alias rustscan='docker run -it --rm --name rustscan rustscan/rustscan:2.0.0'After adding the alias, you can now run commands as:
rustscan -a 192.168.1.0/24 -t 500 -b 1500 -- -AHow to install for Ubuntu
To install RustScan on systems such as Ubuntu and KaliLinux, you can download the .deb file.
As of 30 March 2023, the latest version, which has a downloadable .deb file, is Version 2.0.1.
wget https://github.com/RustScan/RustScan/releases/download/2.0.1/rustscan_2.0.1_amd64.deb
dpkg -i rustscan_2.0.1_amd64.deb
rustscan --help // to test that RustScan is installed on your systemNow you can run RustScan on your system.
RustScan Performance
The best advantage of using RustScan is the speed. RustScan is the fastest port scanner in the wild. It is the fastest because, as the name suggests, RustScan is written in
Rust. Rust is a low-level programming language, just like C. Because it is low-level, it can operate within the network on the lowest level. Being on the lowest level removes the additional overhead some other programming languages have.
Aside from being written in a low-level programming language, RustScan optimizes by scanning ports asynchronously. The Rust programming language lets you run many concurrent tasks on a small number of OS threads. Because RustScan is written in Rust, this holds true as well. Below you can see an animation on how fast a scan of RustScan can be.
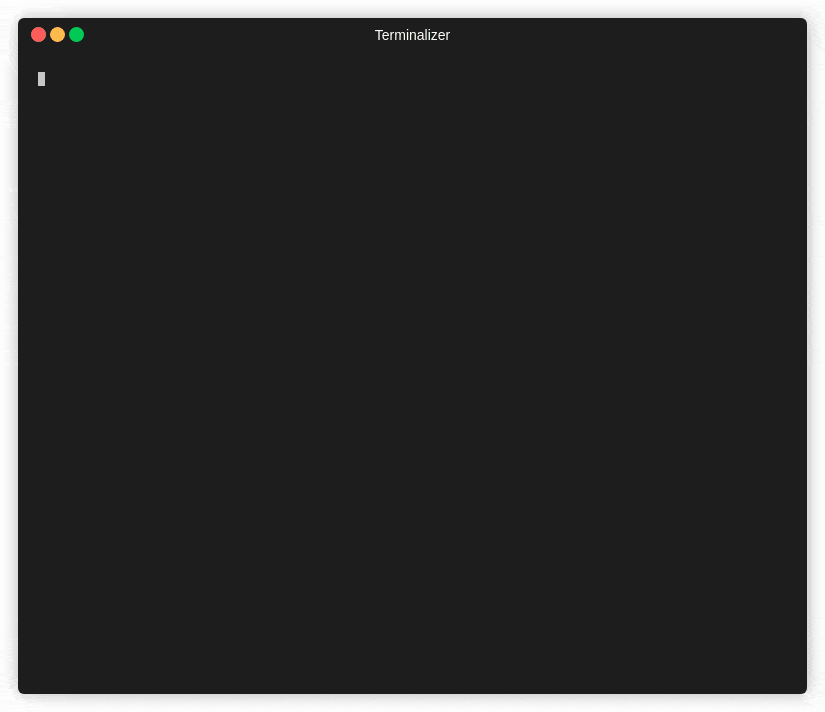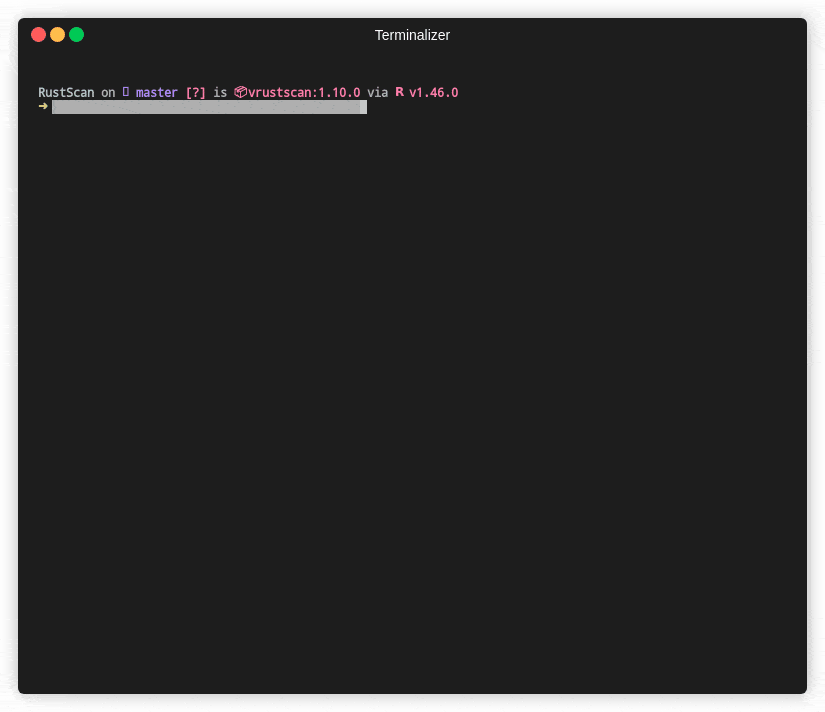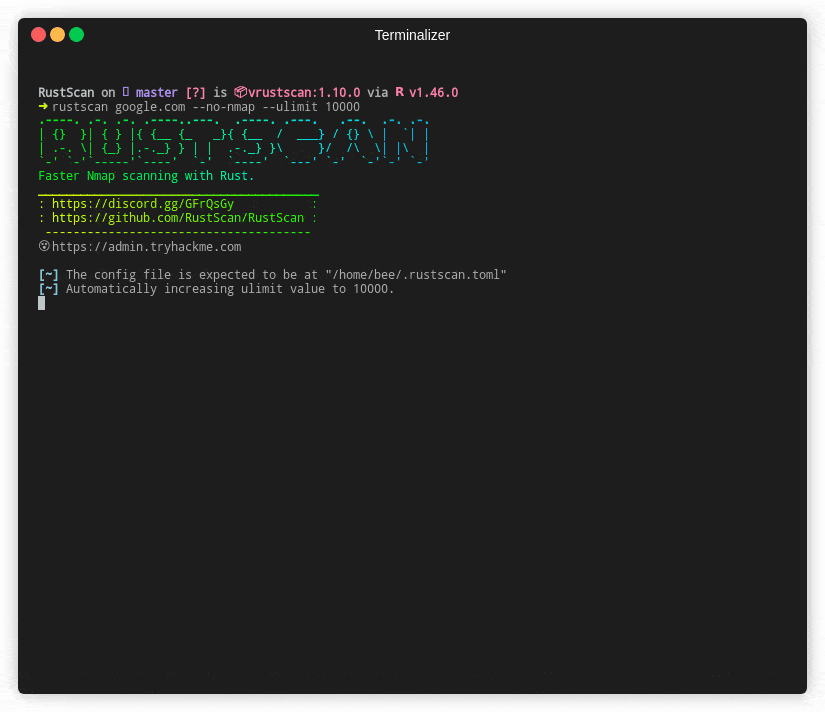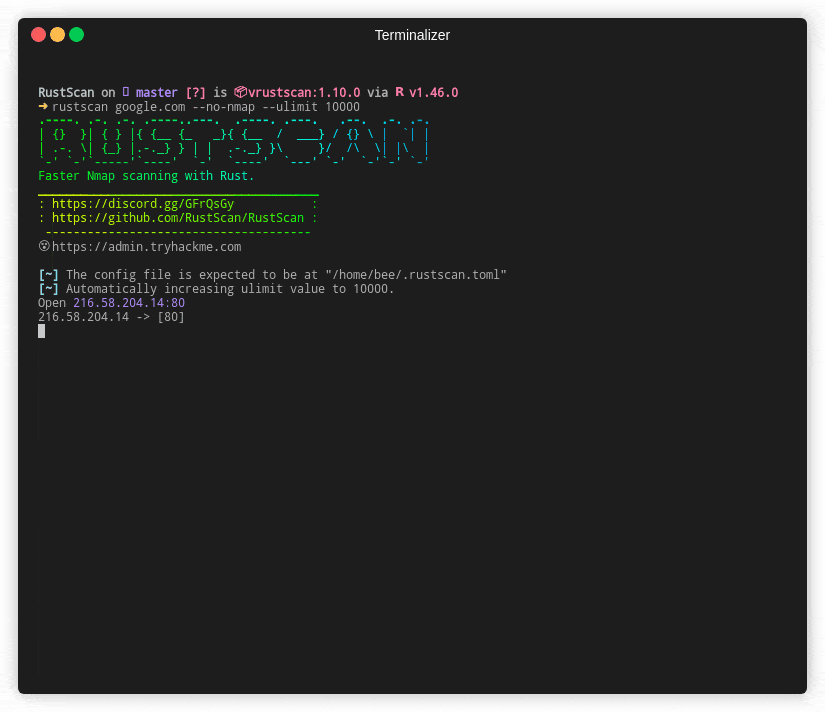
In addition to using Rust and asynchronous scanning, it uses caching to avoid rescanning the same ports multiple times, which can significantly reduce scan times on large networks.
Aside from scanning ports asynchronously, RustScan also scans IP addresses and host names asynchronously. Scanning hosts asynchronously greatly boosts the performance compared to scanners that can only scan hosts synchronously.
One final performance tweak to mention is that the user can also optimize scans performed by RustScan. For example, a user can specify the range of port numbers to scan. Reducing the number of port numbers to scan per system will significantly improve the performance of the port scan as well.
Useful commands
Below you can find some useful commands with an explanation below each snippet.
rustscan -hUse the h flag to find out all options within RustScan.
rustscan -a 127.0.0.1The a flag is used to specify the IP address of the host to scan
rustscan -a 127.0.0.1 -r 0-1000You can set the r flag to specify the range of port numbers you want to scan. In this example from port number 0 to port number 1000.
rustscan -a 127.0.0.1,0.0.0.0You can scan multiple IPs using comma-separated lists
rustscan -a www.google.com,127.0.0.1You can use RustScan to scan domain names as well. Instead of specifying an IP, you add a domain name as a value for the a flag.
rustscan -a 192.168.0.0/30RustScan supports Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation
rustscan -a 'hosts.txt'You can specify a list of hosts in a text file and separate each host by a new line
rustscan -a 127.0.0.1 -p 53You can also specify a single port by using the p flag.
rustscan -a 127.0.0.1 -- -A -sCRustScan also is capable of running nmap scans. For instance here, the sC flag here specifies default scripting. To use nmap parameters, you need to specify -- -A. After this specific flag sequence, all flags are identical to nmap flags.
rustscan -a 127.0.0.1 --range 1-1000 --scan-order "Random"You can scan ports in a random order as well. For this, use the scan-order flag with the value “Random”








